Redirect 404 Errors the Right Way – Avoid the Homepage Trap!
In the world of SEO and website management, encountering 404 errors is inevitable. Every website, no matter how well-maintained, will experience broken links, deleted pages, or outdated URLs that lead users to the dreaded 404 Page Not Found error.
But here’s the deal: how you handle these errors can mean the difference between maintaining your site’s SEO health or unintentionally harming your rankings. Unfortunately, many website owners fall into the common trap of redirecting every 404 error to the homepage, a practice that often confuses users and sends mixed signals to search engines.
Analyze your domain's health score and fix all issues with a single click.

So, what’s the solution? In this guide, we’ll cover:
- Why 404 errors happen.
- The impact of 404 errors on SEO.
- Why homepage redirects are bad practice.
- Best practices for handling 404 errors.
- How to reduce the negative SEO impact of 404 pages.
What Are 404 Errors and Why Do They Happen?
Let’s break it down: A 404 error is an HTTP status code that means the server couldn’t find the requested URL. It doesn’t mean the server is broken, just that the specific page isn’t there. This can happen for several reasons:
- A page was deleted.
- A URL was changed without a redirect.
- A user mistyped a URL.
- Broken inbound or outbound links.
- Incorrectly configured internal links.
Here’s the thing: 404 errors are part of the web’s natural lifecycle. Websites evolve, pages change, and content gets removed. The challenge is managing these errors in a way that preserves user experience and SEO performance.
The SEO Impact of 404 Errors
You might be wondering: Do 404 errors hurt my rankings? Google and other search engines don’t penalize websites for having some 404 errors. However, excessive or poorly managed 404 errors can negatively impact your site’s performance. Here’s how:
1. Wasted Crawl Budget
Google allocates a limited crawl budget to each site. If bots waste time crawling non-existent pages, fewer resources are left to crawl important pages.
2. Lost Backlink Value
If external websites link to a page that now triggers a 404, the SEO value (link juice) of those backlinks is lost. This can weaken your domain authority.
3. Poor User Experience
Landing on a 404 page frustrates users, leading to higher bounce rates. And guess what? A poor user experience can indirectly affect rankings since engagement signals matter.
4. Indexation Issues
If a page returns a 404 but is still indexed, search engines might serve outdated or irrelevant pages in search results.
Why Redirecting 404 Errors to the Homepage Is a Bad Idea
Here’s what Google’s Martin Splitt has to say:
“A 404 is a very clear signal this link is wrong and broken or this URL no longer exists because maybe the product doesn’t exist or something has changed.”
How Redirecting Broken URLs Affects Search Crawlers
When a crawler encounters a proper 404 error, it understands that the page no longer exists and moves on. But if every broken link redirects to the homepage, it disrupts this process, leading to inefficiencies.
Splitt noted:
“For a crawler, they go like a homepage and then click through or basically crawl through your website, finding content, and eventually they might run into a URL that doesn’t exist. But if you redirect, they’re kind of like being redirected, and then it all starts over again.”
Think about it, if users click on a product link and end up on your homepage with no explanation, how would they feel? Confused and frustrated. Not ideal.
So, what should you do instead? Here’s a winning strategy:
Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors (The Right Way!)
So, what should you do instead? Handling 404s correctly is part of good technical SEO hygiene. Below are best practices to manage these errors effectively:
1. Set Up a Custom 404 Page
A custom-designed 404 page keeps users engaged even after they hit a dead end. Your 404 page should:
- Maintain your site’s branding
- Offer clear navigation options (popular pages, site search, menu)
- Provide a friendly, human tone
- Suggest related content or products
- Include a search bar to help users find what they’re looking for
Example: “Oops! The page you’re looking for doesn’t exist. Try searching or check out our latest articles here.”
2. Use 301 Redirects Thoughtfully
Redirects should be relevant and useful. Instead of sending everything to the homepage:
- Redirect to the most relevant page available
- If a product is discontinued, redirect to a similar product or category
- If content was moved, ensure the old URL points to the new one
3. Avoid Blanket Redirect Rules
Here’s a pro tip: Don’t use global rules like “redirect all 404s to the homepage.” Instead, review each error and decide on the best destination.
4. Regularly Monitor 404 Errors
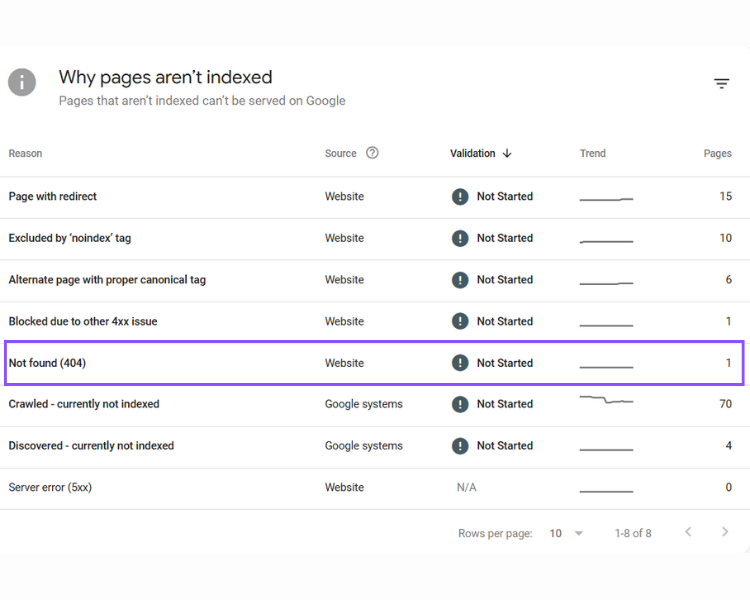 Stay ahead of the game by using tools like:
Stay ahead of the game by using tools like:
- Google Search Console (Coverage Report)
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Ahrefs or SEMrush site audits
Stay on top of new 404 errors regularly and address them quickly to maintain SEO health.
5. Leverage 410 Status for Removed Content
If a page is intentionally removed and won’t return, consider using a 410 Gone status instead of a 404. This tells search engines the content is permanently gone, prompting faster de-indexing.
How to Reduce the Negative SEO Impact of 404 Errors
A well-maintained site doesn’t fear the occasional 404. The real SEO issue is how you handle them. Here are strategies to reduce their negative impact:
1. Audit Internal Links
Regularly audit your internal linking structure. Update outdated links pointing to non-existent pages. Remember, internal links are fully under your control , keep them clean.
2. Reclaim Broken Backlinks
Use backlink tools to find external sites linking to dead pages. Reach out and request updates or set up targeted redirects to preserve link equity.
3. Use Schema Markup on 404 Pages
Adding structured data helps search engines better understand your 404 page content and provides a better user experience.
4. Enhance Site Search
A strong on-site search function can turn a lost visitor into a converted customer. If they don’t find what they came for, help them discover alternative content easily.
5. Create Useful Content Hubs
If you frequently remove old content, consider repurposing it into evergreen content hubs. This reduces the need to delete pages and preserves valuable content and backlinks.
6. Prioritize High-Value 404s
Here’s a pro tip: Not all 404s are equal. Prioritize fixing:
- Pages with backlinks.
- Important landing pages.
- Pages with significant organic traffic history.
Low-traffic 404s from mistyped URLs or outdated parameters are less critical.
Let’s break it down in more detail…
Mistyped URLs Causing 404 Errors
How does this happen?
- A user manually types a URL but makes a mistake.
- A link on another website (or even yours) contains a typo.
Example:
✅ Correct: example.com/best-seo-tips
❌ Mistyped: example.com/best-seo-tip (404 error)
Why is it less critical?
- If very few users type the wrong URL, it doesn’t impact SEO much.
- Google usually doesn’t index mistyped URLs unless they are linked somewhere.
- Instead of wasting time fixing every typo, focus on important 404s (e.g., pages with backlinks).
Outdated URL Parameters Causing 404s
How does this happen?
- Some URLs have extra parameters for tracking, sorting, or filtering.
- If a parameter becomes outdated (e.g., an old campaign link), it may return a 404.
Example:
✅ Working URL: example.com/shoes
❌ Outdated Parameter: example.com/shoes?ref=summer-sale-2023 (404 error)
Why is it less critical?
- The main page (example.com/shoes) still exists and ranks.
- Google usually ignores unnecessary parameters if they don’t affect content.
- Fixing outdated parameters doesn’t improve SEO much unless they have backlinks.
When Should You Take Action?
- If the mistyped URL has backlinks, consider redirecting it.
- If the outdated parameter URL gets traffic, set up a 301 redirect to the correct page.
- If the 404 is truly unnecessary, just let it be, not all 404s need fixing!
Tools to Help Manage and Fix 404 Errors
Want to stay on top of your 404s? Use these essential tools:
- Google Search Console: Identifies crawl errors.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Comprehensive crawl and link checker.
- Ahrefs Site Audit: Finds broken backlinks and internal 404s.
- Google Analytics: Track user behavior on your 404 page to improve design and content.
Final Thoughts: 404s Are Normal – Mismanaging Them Shouldn’t Be!
Let’s wrap it up: No website is immune to 404 errors, but how you handle them sets you apart from competitors. Avoid the lazy solution of redirecting everything to the homepage. Instead, invest in a smart 404 strategy:
- Build a helpful, branded 404 page
- Use targeted 301 redirects
- Monitor errors regularly
- Reclaim lost backlinks
- Improve site navigation and search
By following these best practices, you preserve SEO equity, maintain a positive user experience, and signal to Google that your website is well-maintained and trustworthy.